Alnatura Campus, Darmstadt, Germany
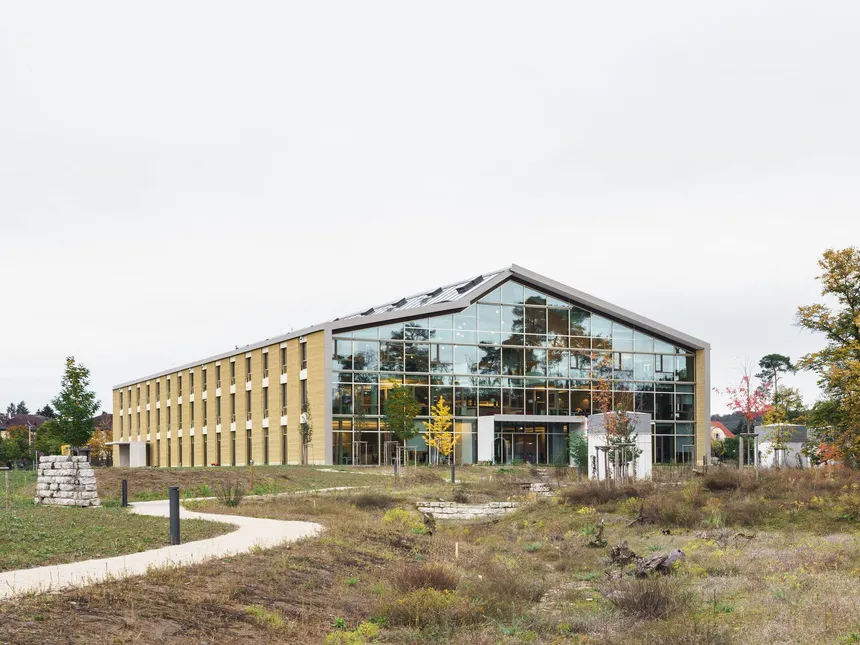


The organic food chain Alnatura has selected in Darmstadt an area of around 50,000 m² on the site of the former Kelley Barracks for its new company headquarters, the Alnatura Campus. The space serves for a public Waldorf kindergarten, a vegetarian organic restaurant, an organic supermarket and also for utility and school gardens to show the cultivation of organic food from sowing to the finished product and last not least for the heart, the very special new headquarter building with ~500 workplaces, Europe's largest office building with façades made from rammed earth.
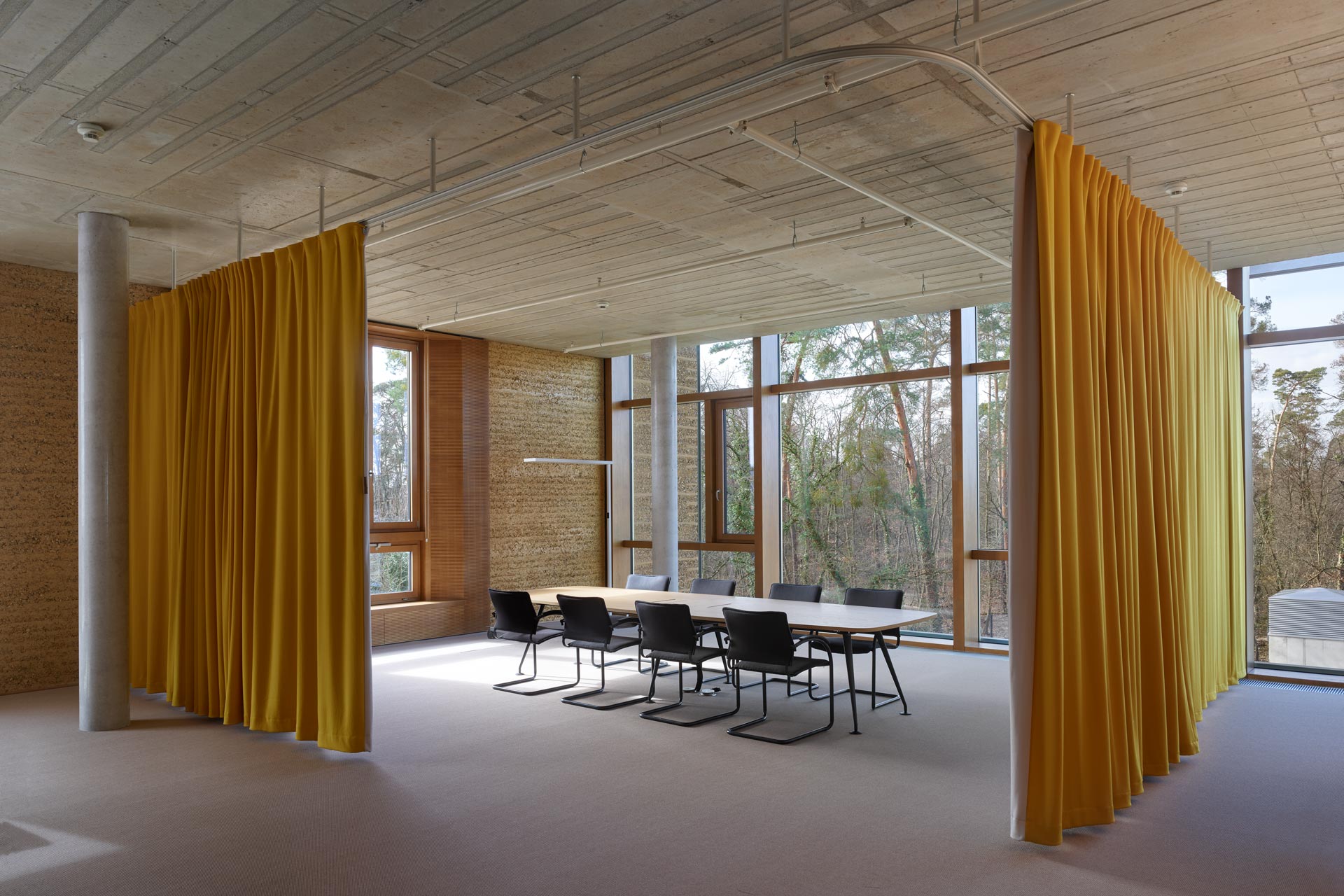
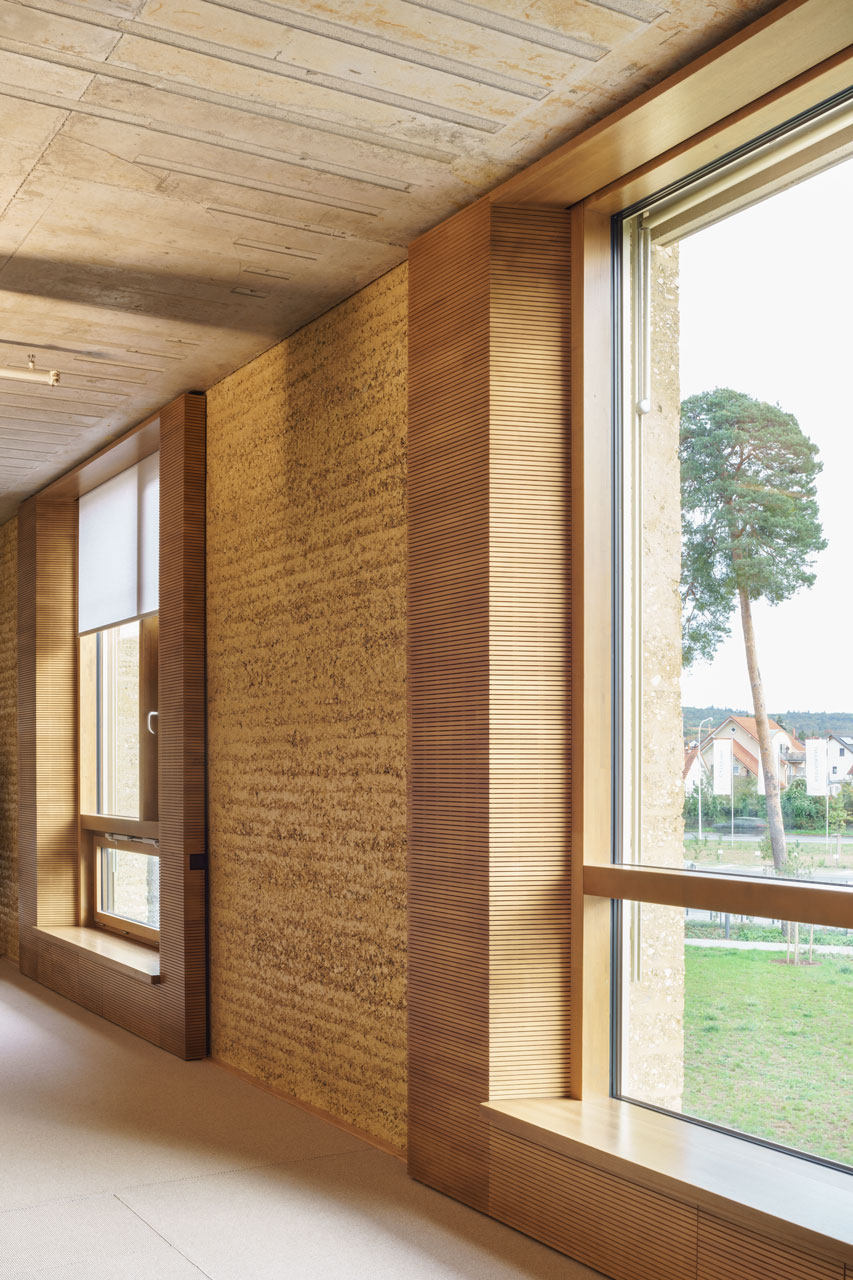
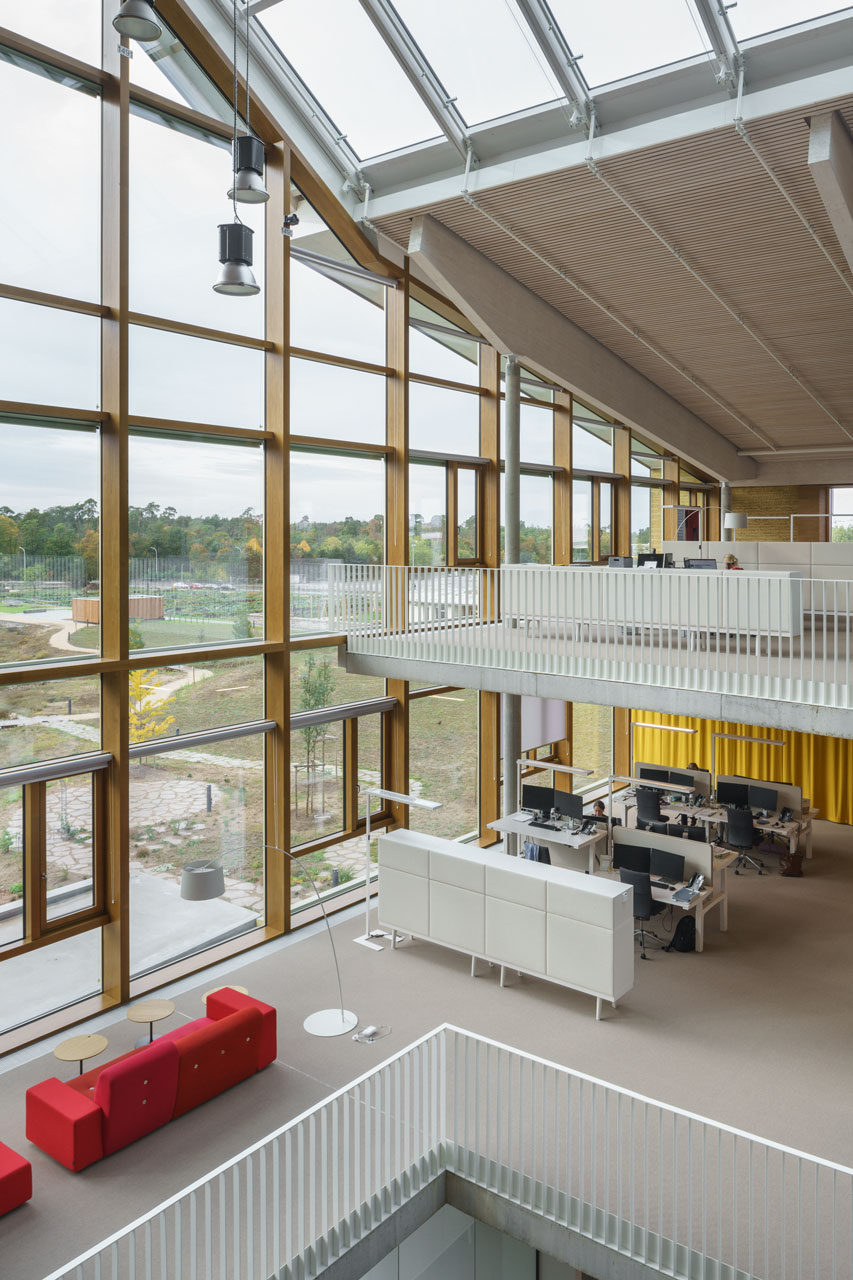
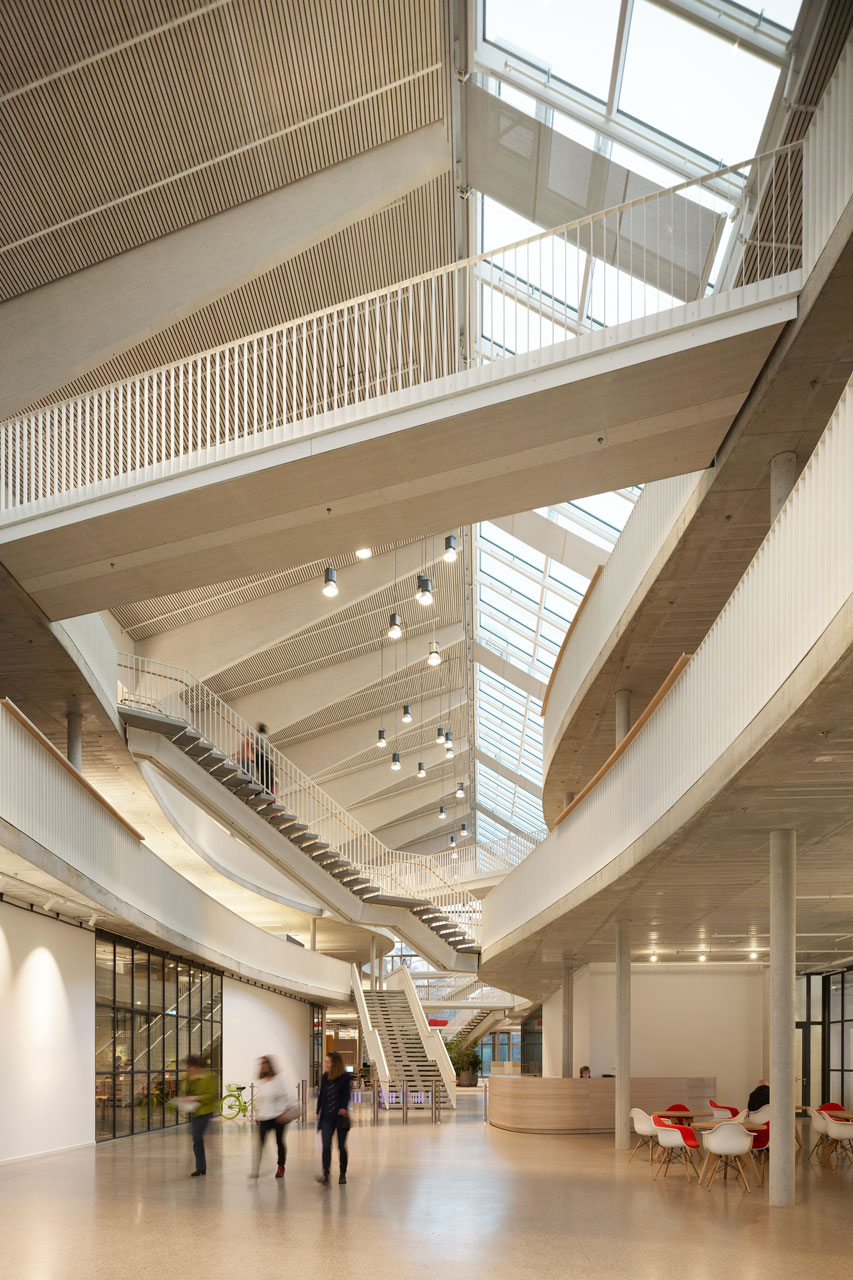
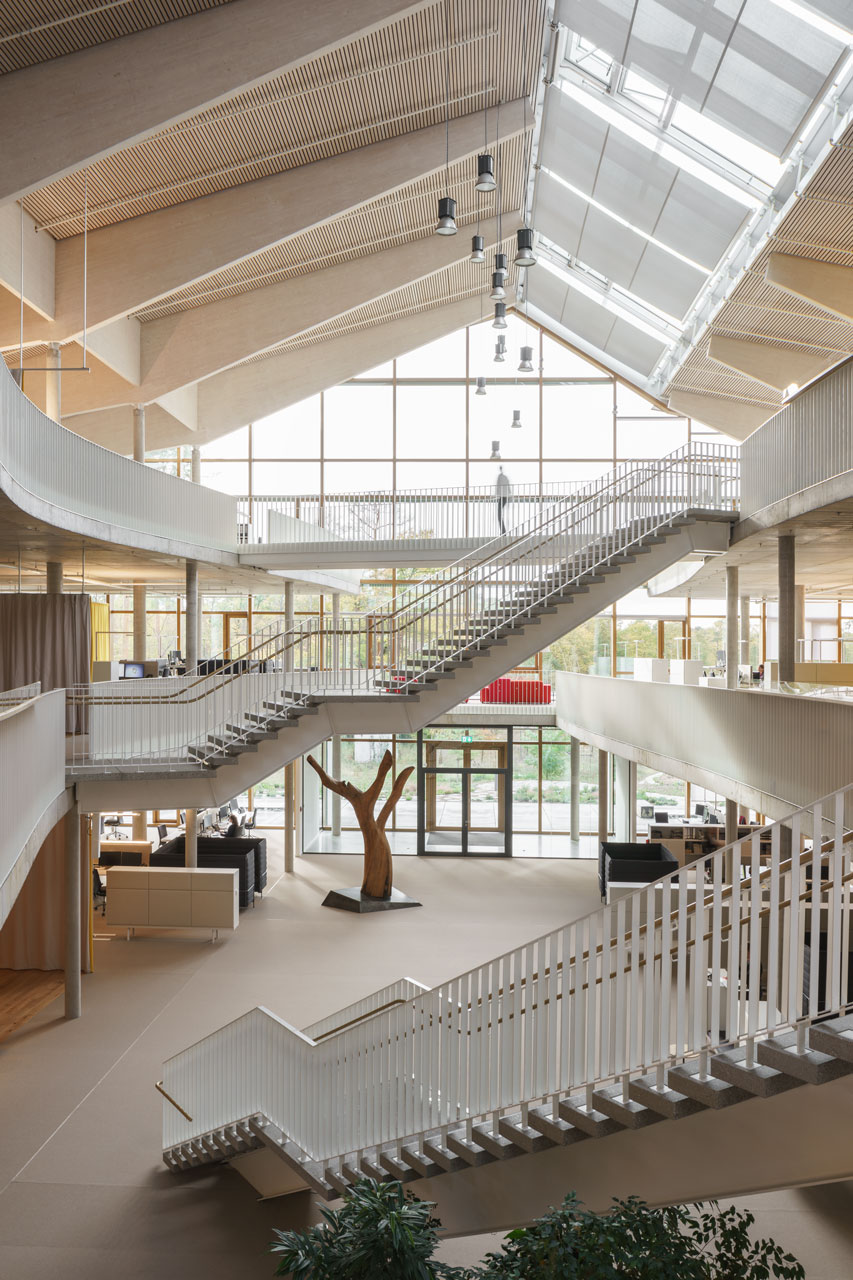
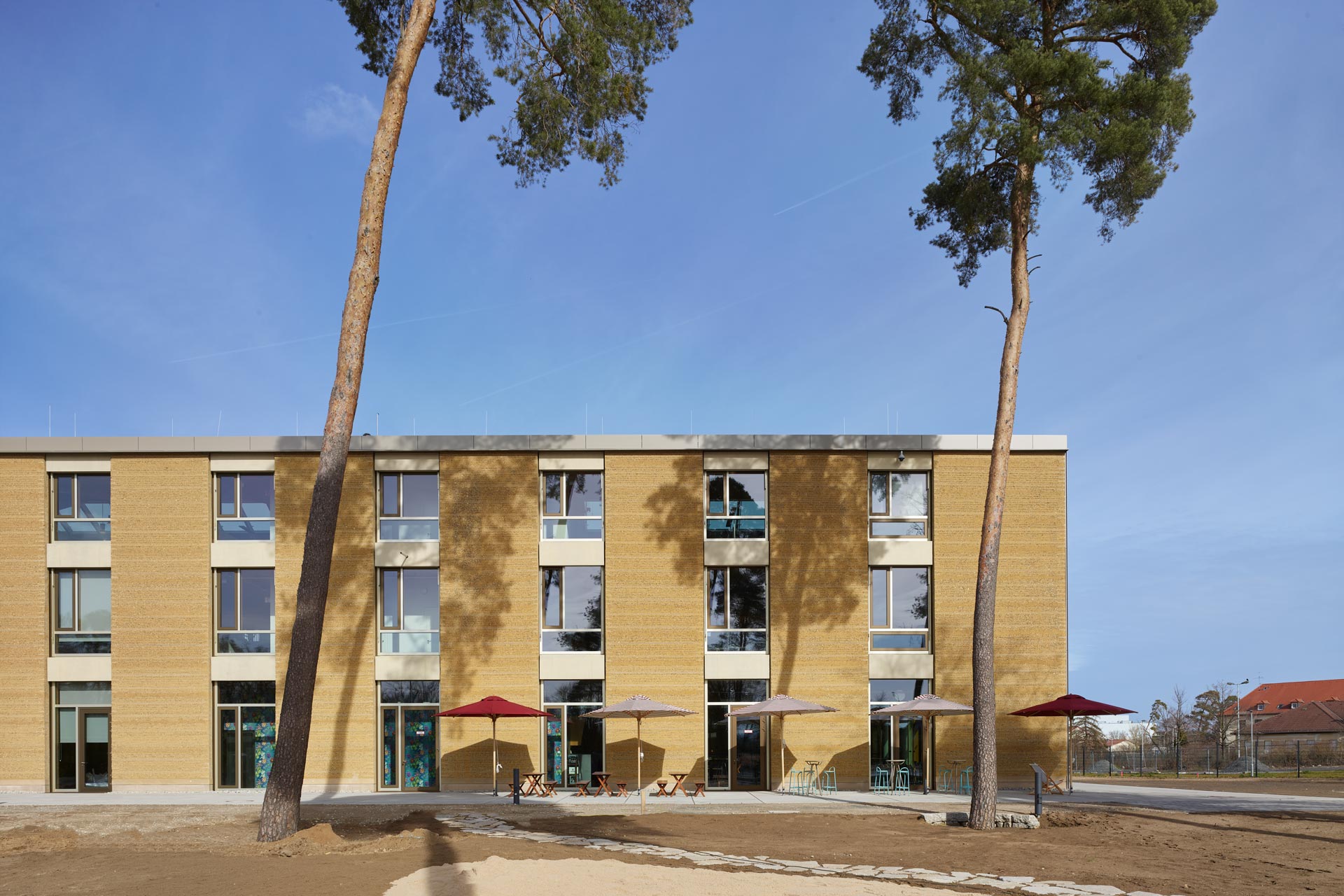
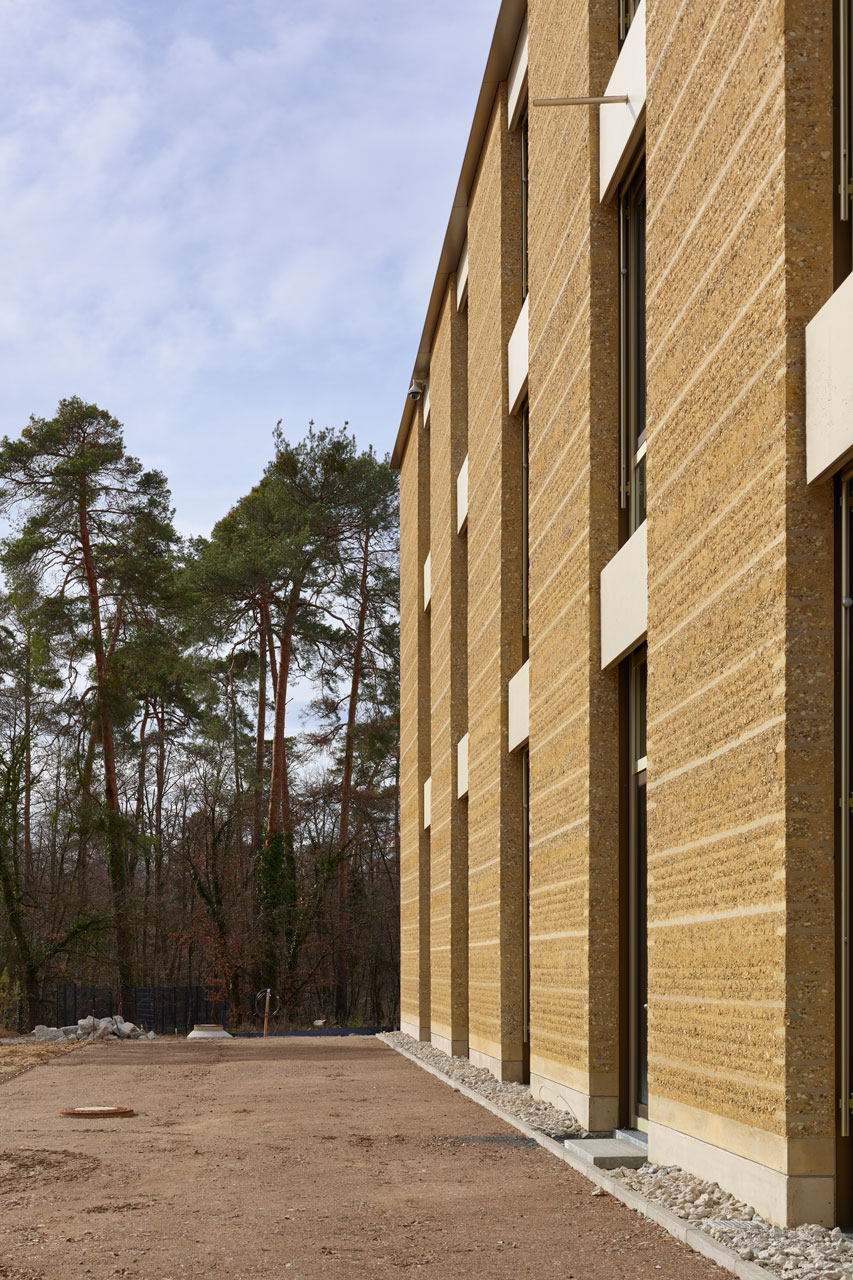
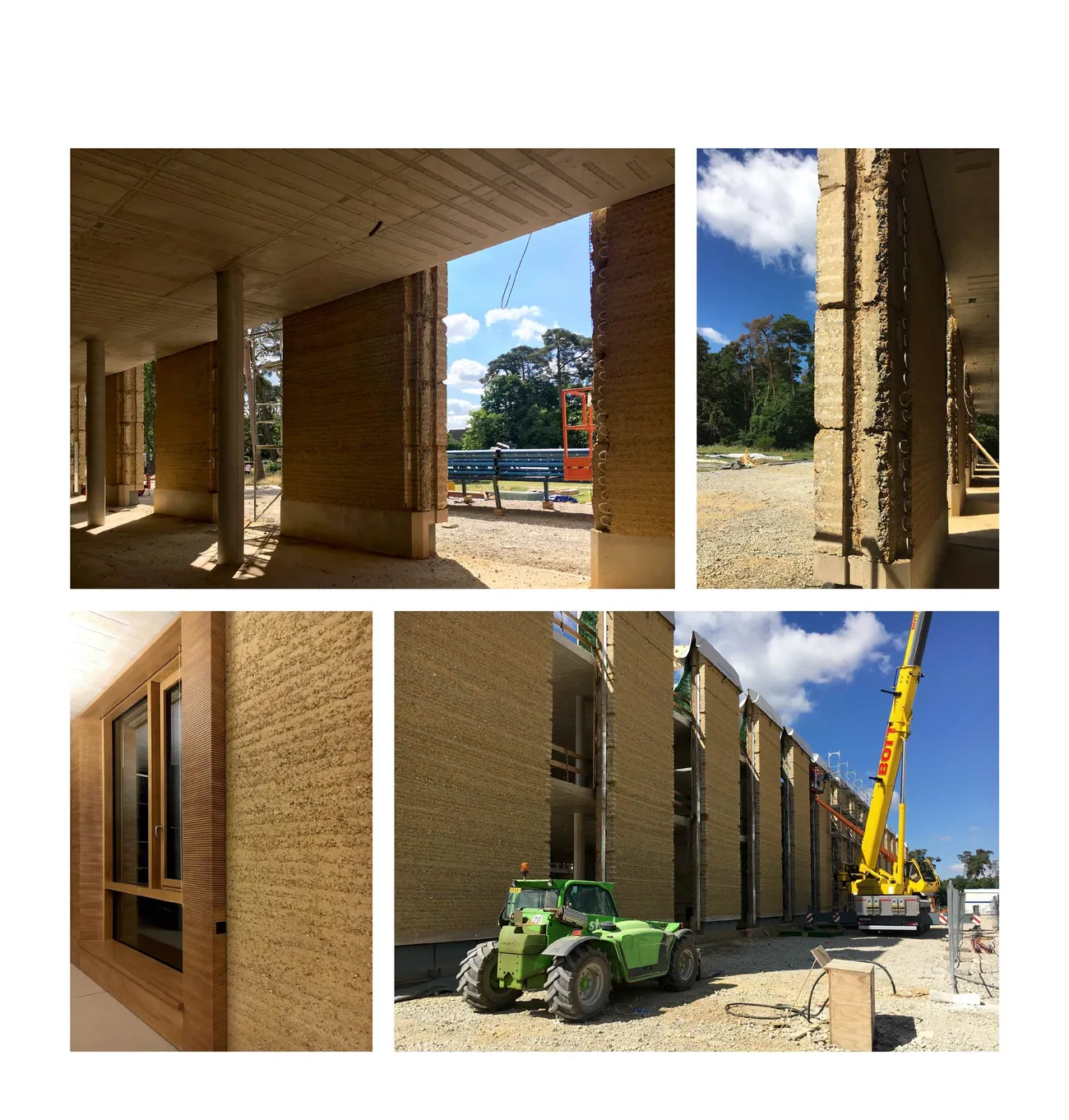
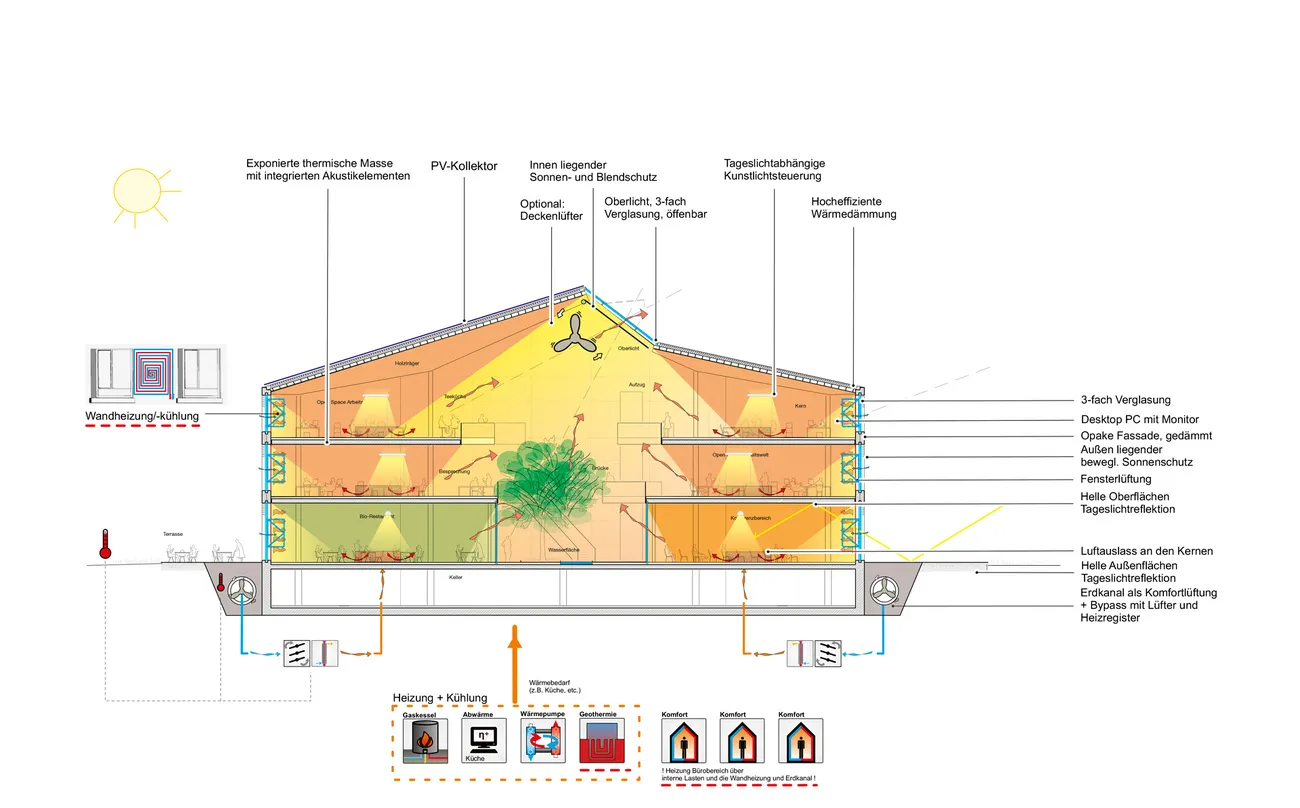
The three-story “Bürowelt” ("office world") is structured into the areas of office, conference and restaurant. In addition to the demand for a good indoor climate, emphasis is placed on "simplicity" in the sense of robustness: more quality through reduction.For example, during the planning phase, care was taken to ensure that passive measures keep the costs for technical systems as low as possible. The gray energy of the new building has also been scientifically evaluated: the amount of energy was investigated which in total is necessary for production, transport, storage, sale and disposal of building materials, what lead to resource-saving solutions for the building components. The result is a high-performance, energy-efficient building with optimized interior comfort made of recyclable or natural materials such as the structure of the gable roof made of wood and the clay facades. A large part of the material for the façade elements made of rammed earth comes from the Stuttgart21 tunnel construction site.
The windows in the clay façades are shaded on the outside. The east and west façades are room-high glazed and, together with the bright surfaces, the atrium and the north-facing skylights, optimally provide daylight. The course of the sun was taken into account in the room layout in order to provide optimal natural light throughout the building. The artificial lighting is regulated depending on usage and daylight. The building is naturally ventilated, with a ground channel preconditioning the fresh air, entering the cores of the office areas via source outlets. Users can also open the windows. Controllable openings in the roof of the atrium serve for ventilation. The system is equipped with CO₂ sensors and is supported with active fans on demand. Solar profits are used deliberately and heat losses are minimized, in order to keep the costs for heating low.
In summer the rooms are cooled by cooling down the thermal mass at night by air flushing. In addition, a radiative system integrated in the space-facing sides of the rammed earth walls as wall heating and direct cooling can be put into operation. The building is supplied with heat and cold from the ground by a system via geothermal probes; photovoltaic panels on the roof generate electrical energy.
2019 'best architects 20' award for office buildings
2019 DGNB Platin
2019 Deutscher Nachhaltigkeitspreis Architektur